Downhole Measurements Laboratory
Long Term Observatories (CORK)
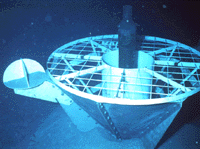 CORKs and ACORKs allow researchers to isolate boreholes from the ocean water above the seabed and monitor conditions in the hole for long periods of time. A CORK's data logger can records temperature and pressure data for five years and store it in memory for an additional five years until it can be retrieved by a manned submersible or ROV. The data are obtained by a string of sensors that hangs from the CORK to the bottom of the borehole. It also has fittings for recovering samples from inside the hole and allows fluid to be injected into the hole for certain kinds of tests. The cork extends above a docking platform for the submersible.
CORKs and ACORKs allow researchers to isolate boreholes from the ocean water above the seabed and monitor conditions in the hole for long periods of time. A CORK's data logger can records temperature and pressure data for five years and store it in memory for an additional five years until it can be retrieved by a manned submersible or ROV. The data are obtained by a string of sensors that hangs from the CORK to the bottom of the borehole. It also has fittings for recovering samples from inside the hole and allows fluid to be injected into the hole for certain kinds of tests. The cork extends above a docking platform for the submersible.
 A CORK's purpose is to provide a long term, seafloor observatory intended to allow a monitored and accessible borehole to return to its predrilling state. Tool specifications can be found in ODP Technical Note 31. A chapter in the Leg 139 Initial Reports volume (Davis, Mottl, Fischer, et al., 1992) describes CORK developement, deployment, and interpretation of preliminary data in some detail. A more complex treatment of CORK postemplacement operations and data interpretation appears in the Leg 139 Scientific Results volume. Additional CORK operations conducted during Leg 146 are described in ODP Technical Note 10. Finally, ACORK operations conducted during Leg 196 are described in the Leg 196 Initial Reports volume.
A CORK's purpose is to provide a long term, seafloor observatory intended to allow a monitored and accessible borehole to return to its predrilling state. Tool specifications can be found in ODP Technical Note 31. A chapter in the Leg 139 Initial Reports volume (Davis, Mottl, Fischer, et al., 1992) describes CORK developement, deployment, and interpretation of preliminary data in some detail. A more complex treatment of CORK postemplacement operations and data interpretation appears in the Leg 139 Scientific Results volume. Additional CORK operations conducted during Leg 146 are described in ODP Technical Note 10. Finally, ACORK operations conducted during Leg 196 are described in the Leg 196 Initial Reports volume.
Modified on Wednesday, 05-Jan-2005 11:51:08 CST.
 CORKs and ACORKs allow researchers to isolate boreholes from the ocean water above the seabed and monitor conditions in the hole for long periods of time. A CORK's data logger can records temperature and pressure data for five years and store it in memory for an additional five years until it can be retrieved by a manned submersible or ROV. The data are obtained by a string of sensors that hangs from the CORK to the bottom of the borehole. It also has fittings for recovering samples from inside the hole and allows fluid to be injected into the hole for certain kinds of tests. The cork extends above a docking platform for the submersible.
CORKs and ACORKs allow researchers to isolate boreholes from the ocean water above the seabed and monitor conditions in the hole for long periods of time. A CORK's data logger can records temperature and pressure data for five years and store it in memory for an additional five years until it can be retrieved by a manned submersible or ROV. The data are obtained by a string of sensors that hangs from the CORK to the bottom of the borehole. It also has fittings for recovering samples from inside the hole and allows fluid to be injected into the hole for certain kinds of tests. The cork extends above a docking platform for the submersible. A CORK's purpose is to provide a long term, seafloor observatory intended to allow a monitored and accessible borehole to return to its predrilling state. Tool specifications can be found in ODP Technical Note 31. A chapter in the Leg 139 Initial Reports volume (Davis, Mottl, Fischer, et al., 1992) describes CORK developement, deployment, and interpretation of preliminary data in some detail. A more complex treatment of CORK postemplacement operations and data interpretation appears in the Leg 139 Scientific Results volume. Additional CORK operations conducted during Leg 146 are described in ODP Technical Note 10. Finally, ACORK operations conducted during Leg 196 are described in the Leg 196 Initial Reports volume.
A CORK's purpose is to provide a long term, seafloor observatory intended to allow a monitored and accessible borehole to return to its predrilling state. Tool specifications can be found in ODP Technical Note 31. A chapter in the Leg 139 Initial Reports volume (Davis, Mottl, Fischer, et al., 1992) describes CORK developement, deployment, and interpretation of preliminary data in some detail. A more complex treatment of CORK postemplacement operations and data interpretation appears in the Leg 139 Scientific Results volume. Additional CORK operations conducted during Leg 146 are described in ODP Technical Note 10. Finally, ACORK operations conducted during Leg 196 are described in the Leg 196 Initial Reports volume.